H–scan
Existing ultrasound imaging technology is insufficient for certain disease diagnosis (such as tumors). The H-Scan ultrasound imaging algorithm (‘H’ represents Hermite or hue) can show the particles of suspected organ tumors, providing more reliable medical diagnostic evidence for disease conditions (this imaging diagnostic technology is a new one in medical imaging research).
However, current H-Scan ultrasound imaging process takes a long time, and the signal processing speed before acceleration is only 8fps, which cannot meet real-time display requirements. Through acceleration of Lingyange’s HPC (high performance computing) system, the medical imaging processing time and the H-Scan algorithm can be accelerated to 24fps to meet the goal of real-time display and effective discrimination. Lingyange’s HPC system can process a greater amount of H-Scan data at the same time and improve real-time diagnostic capabilities.
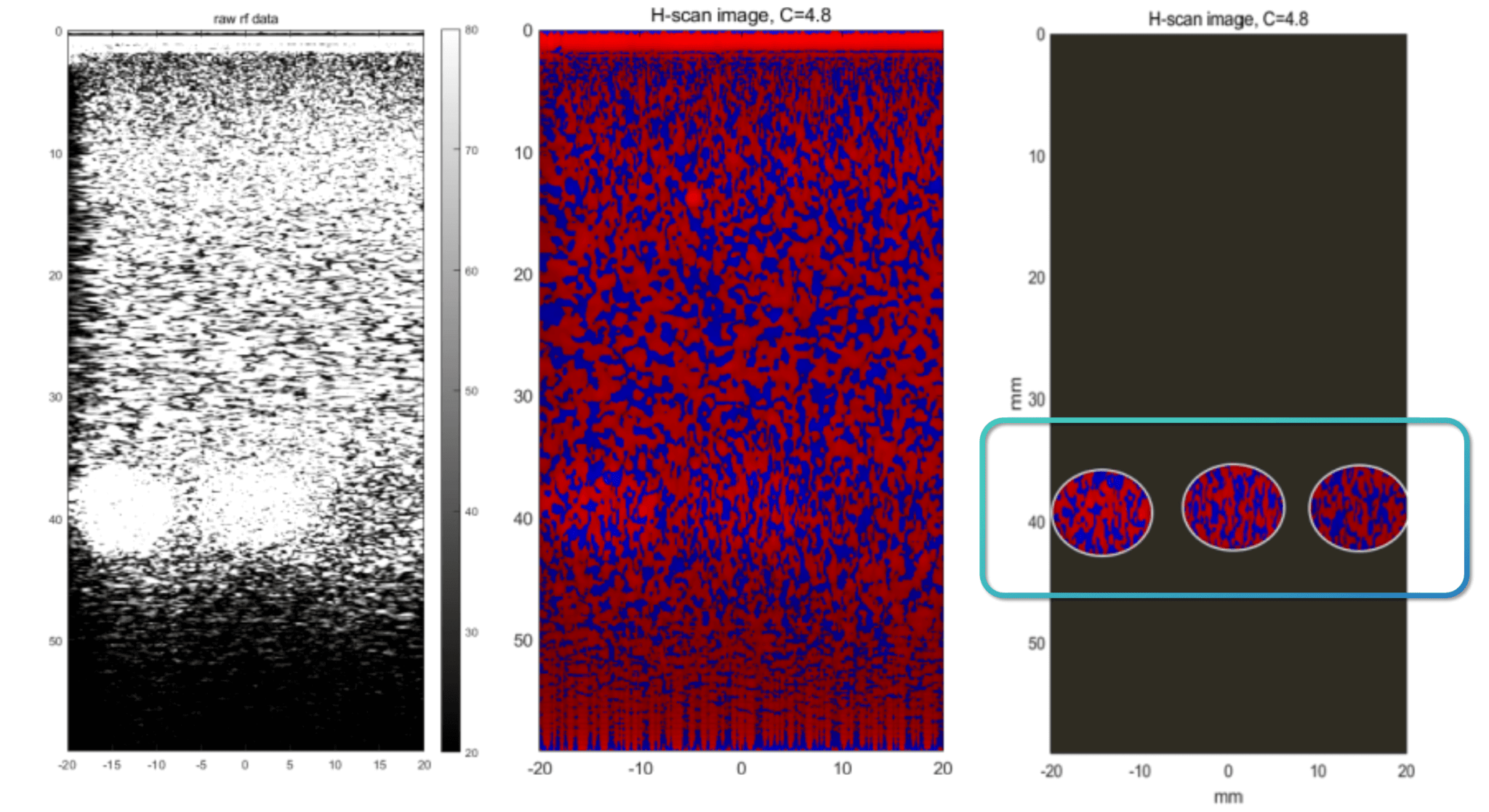
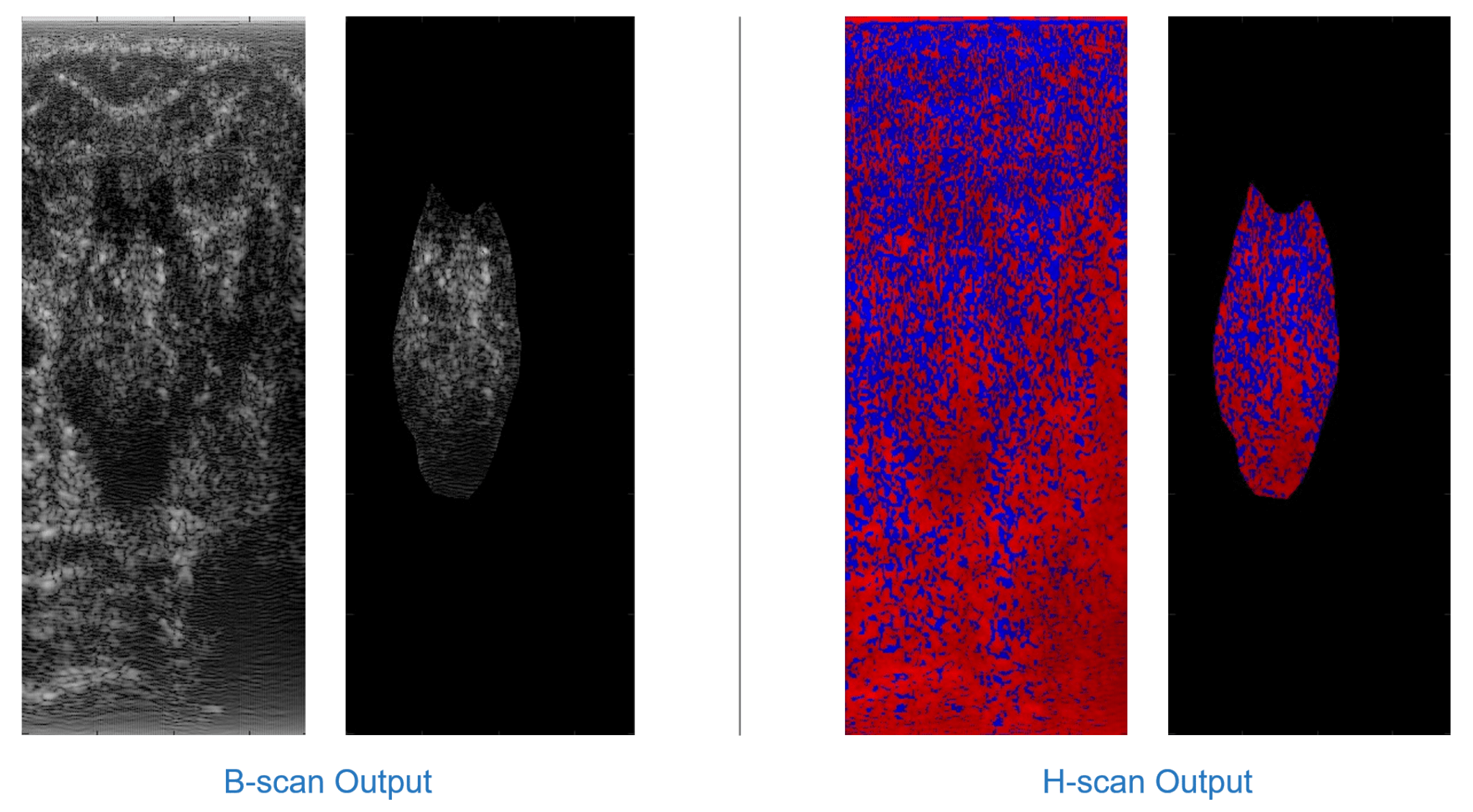
Comparison of regular ultrasound imaging and H-scan imaging
Taking the analysis of breast tumors using the Hermite Scan (H-Scan) ultrasound imaging technique as an example, the benign red component is higher than the blue component, while the malignant is the opposite.
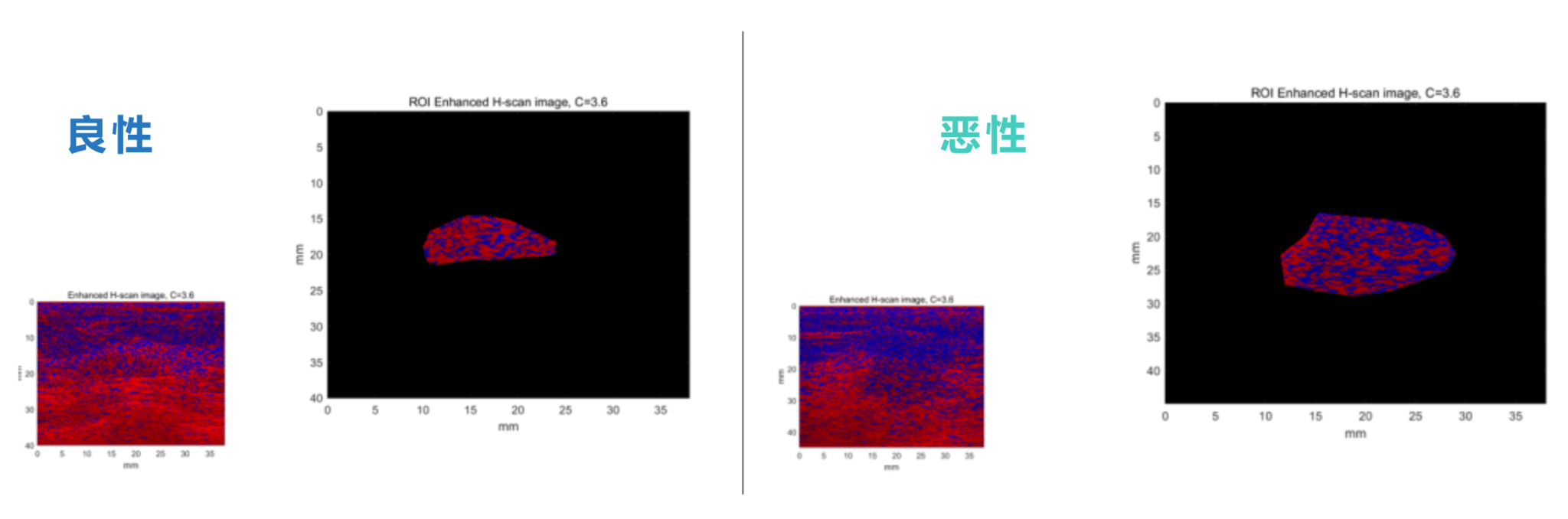
Breast tumor imaging
Lingyange’s HPC system consists of an chiplet accelerator board (BF400) and software operators for signal processing. The goal is to shorten the H-Scan ultrasound imaging time for faster medical diagnosis (targeting 24fps).
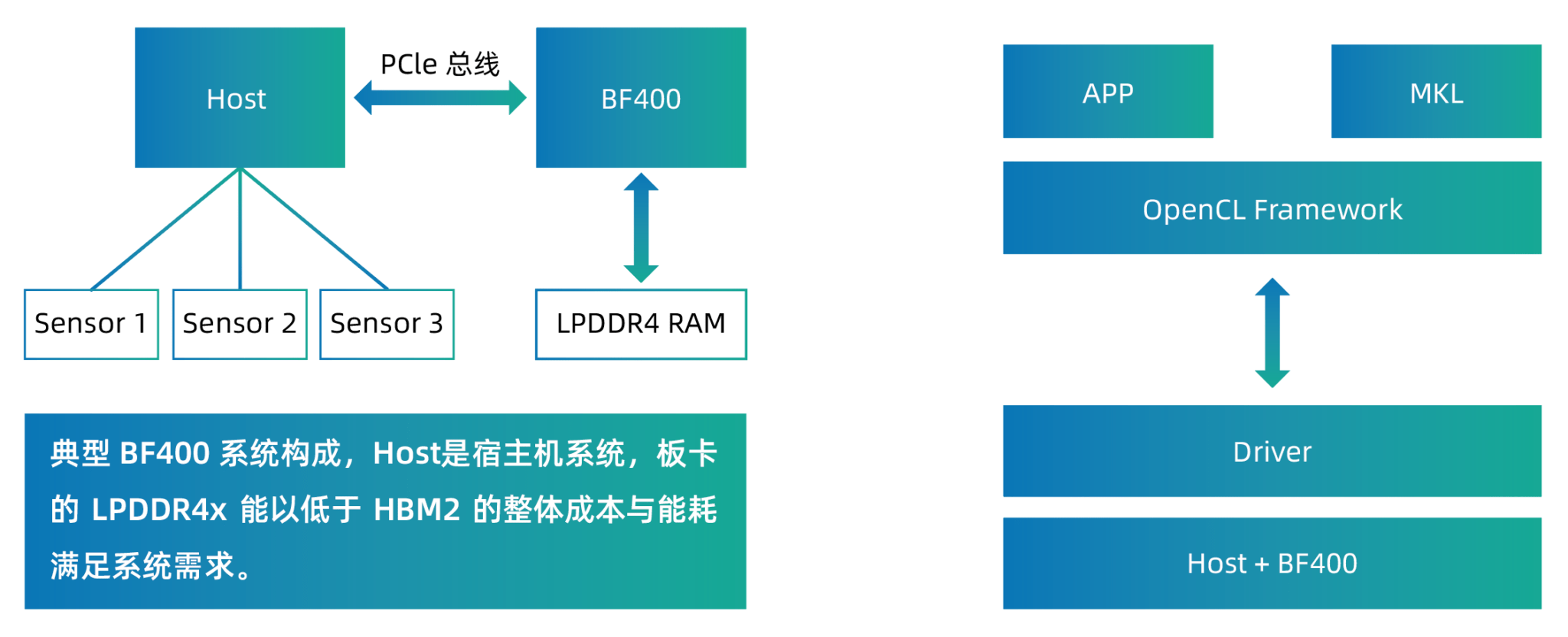
BF400 supports OpenCL, Intel Math Kernel Library (MKL), Matlab toolbox, and commonly used signal processing operator libraries.
Chiplet accelerator board
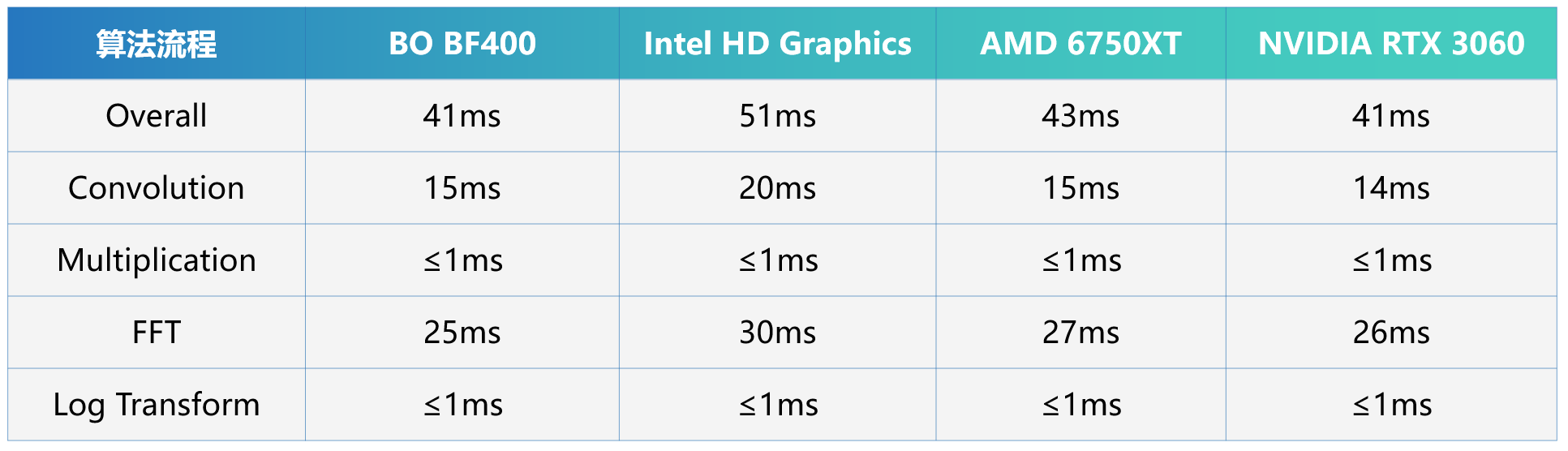
The following calculation results show that the H-Scan algorithm correctly displays results on Lingyange’s HPC system, with a signal processing speed of approximately 40-42 ms, achieving the target of 24 fps. Compared with other acceleration cards, the signal processing speed of Lingyange’s HPC system is similar to NVIDIA and other accelerated platforms.
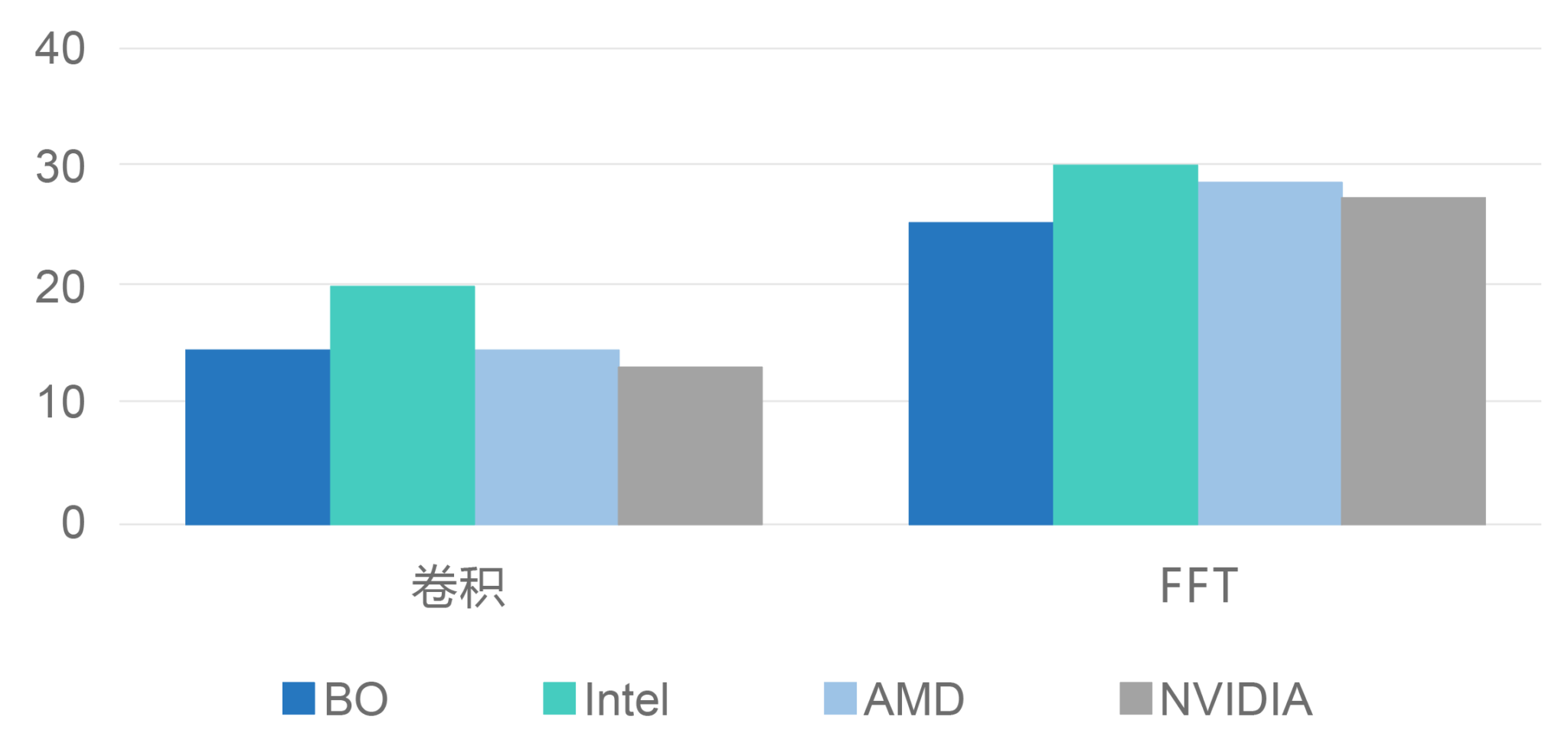
Average calculation time (ms)